
Image generated by Canva. Prompt: „Learning 'prompting’ in creating professional images. Strategies for issuing commands to artificial intelligence systems to make it effective.”
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an indispensable tool in today’s world of creating professional images. With the development of generative models, AI offers new possibilities for artists, designers, and visual creators. However, to achieve the desired results, a key issue is the process of „prompting” these systems.
Prompting is the art of formulating instructions or suggestions for algorithms to help them generate expected content in a creative and consistent manner. Every AI tool, especially those based on generative models, operates by responding to specific inputs, known as „prompts”. Depending on the specifics of each model, the interpretation of prompts may vary.
In this article, we will explore this issue from the perspective of effective prompting strategies, which can not only make the process of creating images more efficient but also align it with social and ethical values. It’s crucial to understand that there are various approaches to prompting, and choosing the right strategy can significantly impact the final outcome.

For instance, in the case of generative language models like GPT-3, a well-crafted prompt can prompt the system to generate content aligned with user expectations. Meanwhile, for visual generative models like DALL-E, prompting may involve specific visual descriptions to be realized.
Modern AI tools require users to deeply understand their operation and capabilities. Therefore, achieving optimal results entails not only skillful prompt formulation but also continuous improvement of the prompting process through experimenting with different approaches and strategies.
Moreover, the ethical aspect of prompting is becoming increasingly important. As AI advances, questions arise about the responsible use of these technologies. Thus, alongside effectiveness and efficiency, it’s essential to be guided by social and ethical values when prompting artificial intelligence systems.
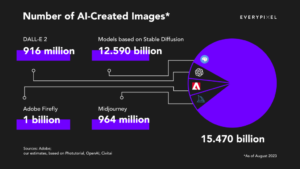
Increase in Text-to-Image Algorithm Usage:
- Since last year, over 15 billion images have been created using text-to-image algorithms, surpassing the growth rate of photography over 150 years.
- DALLE-2 Usage Growth: DALLE-2 generates an average of 34 million images per day since its launch.
- Dynamic Development of Adobe Firefly: Adobe Firefly reached 1 billion created images just three months after its launch.
- Largest User Base on Midjourney: Midjourney has 15 million users, constituting the largest user base among image generation platforms.
- Stable Growth in Stable Diffusion Usage: Approximately 80% of images were created using Stable Diffusion, open-source software.
For more information, please visit: ai-image-statistics
Understanding the Theoretical Foundations of Prompting
The foundation of prompting in the context of artificial intelligence lies in a deep understanding of the mechanisms of generative models responsible for creating images based on provided instructions. In literature, such as the works of Brown et al. (2020) and Radford et al. (2019), the importance of precise instructions and their impact on the quality of generated images is emphasized.



The image generated by the prompt „monkey astronaut” by (from left) Midjourney, Canva, DALL-E



The image generated by the prompt „A synthwave style sunset above the reflecting water of the sea” by (from left) Midjourney, Canva, DALL-E



The image generated by the prompt „A handpalm with a tree growing on top of it” by (from left) Midjourney, Canva, DALL-E
It can be observed that each image-generating platform adopts a different approach to creation. Some focus on directly tailoring images to descriptions, while others generate images based on specific keywords.
In the processing mechanism of models, there’s a complex process enabling them to interpret and understand prompts. Through learning from extensive datasets, models can generate new content, including images, according to provided prompts.
One of the key theoretical aspects of prompt foundations is understanding how model parameters influence their operation. For instance, the generation temperature in generative models determines how „creative” or „conservative” the content generation process will be. Lower temperature may lead to more predictable and „safe” results, while higher temperature may result in more experimental and surprising outcomes.
Experimenting with various model parameters, such as generation temperature or prompt length, allows for a better understanding of how they affect the image creation process by artificial intelligence. By exploring these parameters, users can tailor model operation to their specific needs and preferences.
Understanding the theoretical foundations of prompting is crucial for effectively harnessing the potential of artificial intelligence in image creation. This not only leads to better results but also ensures the preservation of social and ethical values, which may be significant in the context of using artificial intelligence in art and design.
The Golden Mean between Control and Creativity in the Prompting Process

Analyzing the prompting process, it is crucial to find the right balance between control and creativity. This balance is the key component that determines the effectiveness and satisfaction with the obtained results.
The effectiveness of prompting largely depends on the clarity and precision of the provided instructions, as mentioned earlier. Well-formulated prompts enable artificial intelligence to generate content consistent with the user’s intentions. However, it is equally important for prompts not to be too restrictive. Overly defined instructions can result in repetitive or predictable outcomes, limiting the algorithm’s creativity.
On the other hand, overly loose or general prompts can make it difficult for algorithms to interpret and generate the desired content. This is particularly significant in the context of artistic projects where creativity and originality are crucial.

Finding the golden mean between control and freedom in the prompting process becomes a critical challenge. It’s worth noting that the approach to prompting should be flexible and tailored to the specific project and expectations for the results.
Therefore, conscious utilization of various prompting strategies, considering both control and allowing room for the algorithm’s creativity, can lead to optimal outcomes. Such practice not only facilitates achieving satisfactory results but also promotes the development of ethical and responsible artificial intelligence.
Strategies for Introducing Commands to Artificial Intelligence Systems
Introducing precise commands into artificial intelligence systems is a crucial step in the prompting process that significantly impacts the quality of generated images. Below, we will discuss in detail strategies that can be effectively utilized in this process, considering both technical and social aspects.
One of the key elements of effective prompting is the clear formulation of instructions. The user should precisely specify what they expect from the AI system, avoiding unclear or ambiguous commands. For example, instead of a simple suggestion like „draw a tree,” a better prompt might be „draw a tall, green tree with sprawling branches, standing in a meadow full of flowers.”


„Tree” and „Tall, green tree with spreading branches, standing in a meadow full of flowers.”
Clarity and precision in instructions are crucial for effective prompting. Providing AI systems with clear guidelines enables them to effectively generate the expected content. In the literature, such as the works of Brown et al. (2020) and Radford et al. (2019), the importance of this clarity and precision is emphasized. Researchers point out that unclear or imprecise instructions can lead to undesired outcomes or interpretations, significantly reducing the efficiency of the image generation process by artificial intelligence.
In light of these findings, it is essential to formulate instructions in a way that precisely defines the desired characteristics of the generated image. When creating prompts, it is worth considering all relevant details regarding the context, topic, and intended atmosphere. At the same time, unnecessary complexity should be avoided to not hinder the understanding of the instructions by the AI system.
Well-formulated instructions not only facilitate the work of algorithms but also help users achieve the desired results from prompting. In practice, carefully refining the commands can significantly impact the quality of generated images, eliminating potential ambiguities and lack of precision that may arise during the creation process.

During prompting of artificial intelligence systems, it is important to consider the context in which the image is to be generated. Context includes a variety of factors such as the topic, style, intended emotions, or atmosphere, which should be adequately reflected in the instructions for the AI model.
For example, if a user intends to generate an image related to nature, the instructions should include details about the environment, such as the type of landscape (e.g., mountains, forests, sea), weather conditions (sunny, rainy, cloudy), and characteristic elements (e.g., birds, animals, plants). Additionally, incorporating colors and the atmosphere of the surroundings can further complement the instructions to ensure that the generated image is cohesive and reflects the intended aesthetic.


A key aspect of considering context is adjusting the instructions to the user’s intentions and expectations regarding the final outcome. This allows the generated image to be more relevant and satisfying for the user.
Furthermore, when creating instructions, it is important to consider social and cultural context as well. Certain motifs, themes, or styles may be more appropriate in specific social contexts, so it is valuable to be aware of the preferences and expectations of the target audience.
In practice, considering context requires users to have the ability to precisely describe the intended image and awareness of the impact of various factors on the final result. However, well-formulated instructions tailored to the context can significantly increase the effectiveness of prompting and the quality of generated images.
Ethics and Social Responsibility

Practical Methods and Tools for Prompting Artificial Intelligence Systems



However, when we precisely define our expectations, for example, „hot dog in Manhattan – a picture of a typical New York hot dog against the backdrop of a crowded street,” the artificial intelligence system will be able to better understand our needs and provide more relevant results.


Clear instructions allow the AI system to better understand user expectations and respond more precisely to queries. They help avoid misunderstandings and generate more relevant visual content. In the literature, such as the works of Brown et al. (2020) and Radford et al. (2019), the importance of clear and precise instructions as a key element of effective prompting is emphasized.
In practice, using clear instructions can be supported by examples, illustrations, or specific guidelines regarding what is expected from the generated image. This enables the user to better define their needs, and the AI system can provide more satisfying results.
Clear and precise instructions are a fundamental part of the prompting process, significantly influencing the quality of generated images and the degree of alignment with user expectations.
Utilizing Specialized Platforms
Currently, there are specialized platforms and tools dedicated to prompting artificial intelligence systems. These platforms offer user interfaces that facilitate the formulation of instructions and experimenting with various parameters and settings of AI models. Examples of such platforms include OpenAI’s DALL-E, Canva, Midjourney, Adobe Firefly, which enable the generation of images based on textual descriptions.
Experimenting with Model Parameters
Experimenting with different parameters of AI models can have a significant impact on the generated images. Parameters such as generation temperature, prompt length, or number of iterations can influence the style, quality, and diversity of the generated images. Trying out different combinations of parameters can help users find optimal settings for a specific project or task.


Analysis of Results and Drawing Conclusions
After completing the prompting process, it is essential to carefully analyze the results and draw appropriate conclusions. The analysis involves evaluating the quality of the generated images, identifying any errors or imperfections, and drawing conclusions about the effectiveness of the applied prompting strategies. Based on this analysis, users can adjust their approaches and improve the prompting process in the future.
Specific Use Cases
Art
 In the field of art, artificial intelligence systems are used to experiment with new forms of artistic expression. For example, an artist may use a platform to generate artistic concepts based on textual descriptions. This approach enables the exploration of creative ideas and inspirations, which can then be further developed in traditional artistic media.
In the field of art, artificial intelligence systems are used to experiment with new forms of artistic expression. For example, an artist may use a platform to generate artistic concepts based on textual descriptions. This approach enables the exploration of creative ideas and inspirations, which can then be further developed in traditional artistic media.
Graphic Design
In the graphic design industry, artificial intelligence systems can be used to generate graphics and illustrations for various projects. For example, a designer can use generative models to quickly create prototypes of user interfaces, advertising graphics, or visual elements for websites.
Scientific Research

In scientific research, artificial intelligence systems are used for data analysis, mathematical modeling, and generating scientific visualizations. For example, researchers can use AI models to generate graphics presenting the results of experiments, spatial data analysis, or simulations of physical phenomena. Such visualizations can help in better understanding and communicating complex scientific concepts.
The practical applications of these methods and tools in various fields demonstrate that artificial intelligence systems have the potential to revolutionize the way we create and interpret visual content. They enable faster, more creative, and effective creation of graphics, images, and visualizations, opening up new possibilities for both professionals and amateurs in the fields of art and design.
Summary

In this article, we delved into the topic of „Optimal Prompting Strategies in Creating Professional Images Using Artificial Intelligence.” We understood that prompting is a key element in the process of utilizing artificial intelligence systems for generating visual content.
Starting from the analysis of theoretical foundations of prompting, we noticed that precise formulation of instructions, understanding the mechanisms of AI models, considering context, and adhering to ethical principles are crucial for achieving desired results.
We also examined practical methods and tools for prompting, such as clear instructions, the use of specialized platforms, experimenting with model parameters, and result analysis. We highlighted specific fields where artificial intelligence systems find practical applications, including art, graphic design, and scientific research.
Guiding Thought
During the exploration of optimal prompting strategies in creating professional images using artificial intelligence, we notice that this is a dynamically evolving area that offers many possibilities. However, it is equally important to adhere to ethical principles, consider context, and continually improve the prompting process.
Conclusions

The future of prompting in creating images using artificial intelligence appears promising. AI tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated, opening new horizons for artists, designers, and scientists. However, it is equally important to develop ethical awareness and a responsible approach to using these technologies.
Understanding and utilizing optimal prompting strategies can contribute to the creation of high-quality, creative visual content that reflects our values and goals. The key to success lies not only in innovation in leveraging artificial intelligence but also in compliance with social and ethical norms.
Ultimately, the future of prompting in artificial intelligence depends on our understanding, creativity, and awareness, as well as on continuous technological and normative development in the field of artificial intelligence.
Literature:
The following sources were used while writing this article:
- Brown, T. B., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P., … & Amodei, D. (2020). Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.14165.
- Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., & Sutskever, I. (2019). Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI blog, 1(8), 9.
- GPT-3: Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. OpenAI, 2020.
- Brock A., Donahue J., Simonyan K. (2018). Large Scale GAN Training for High Fidelity Natural Image Synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.11096.
- Radford A., Wu J., Child R., Luan D., Amodei D., Sutskever I. (2019). Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. OpenAI.


